How to deploy Mattermost in docker swarm behind Caddy v2.4.5
-
 Rajasekhar Gundala
Rajasekhar Gundala - 10 Sep, 2021
Mattermost is the leading open source collaboration platform written in Golang and React and runs as a single Linux binary with MySQL or PostgreSQL. This post is to deploy Mattermost in docker swarm behind Caddy 2.4.5
In this post, I am going to show you how to deploy Mattermost in our Docker Swarm Cluster using the Docker Compose tool.
Mattermost is the only Open Source Collaboration Platform for Developers. Bring your tools and teams together in a fully secure location.
Mattermost offers an open-source, high-trust, developer-centric approach to collaboration
Mattermost is an open-source platform that is supported by a large community with 600 integrations and counting. Using an open-source platform allows the development teams to build high-performance workflows for DevOps, ChatOps, conversational development, and continuous deployment while maintaining complete code audit and control over the service’s technical roadmap.
Mattermost helps teams deliver high-quality software while meeting the safety, privacy, and scale requirements of IT and security teams.
Mattermost on-premises and secure SaaS deployments provide the benefits of modern communication without sacrificing privacy.
Let’s start with actual deployment…
Prerequisites
Please make sure you should fulfill the below requirements before proceeding to the actual deployment.
- Docker Swarm Cluster with GlusterFS as persistent tool.
- Caddy as reverse proxy to expose micro-services to external.
Introduction
Mattermost is a modern communication platform behind your firewall. Run team communications under your existing security and IT policies.
DevOps teams use Mattermost to power collaboration at every stage of the DevOps lifecycle. Mattermost unifies people, tools, processes, and automation to help your team increase innovation and agility.
The rock solid code base and large global community will help you to build web sites fast.
Please go through the below links if you want to know more about Mattermost
Mattermost Features
Mattermost is the leading open source collaboration platform with a thriving community, written in Golang and React and runs as a single Linux binary with MySQL or PostgreSQL as database server.
It has the features file sharing, real-time group chat, and webhooks with full access to source code.
Use Mattermost Team messaging feature to streamline coordination while maintaining control and security.
Find the below features of Mattermost.
- Open Source
- Security
- Privacy
- Legal Compliance
- Extensibility
- Scalability
Learn more about Mattermost features going through official link below.
https://mattermost.com/product/
Persist Mattermost Data
Containers are fast to deploy and make efficient use of system resources. Developers get application portability and programmable image management and the operations team gets standard run time units of deployment and management.
With all the known benefits of containers, there is one common misperception that the containers are ephemeral, which means if we restart the container or in case of any issues with it, we lose all the data for that particular container. They are only good for stateless micro-service applications and that it’s not possible to containerize stateful applications.
I am going to use GlusterFS to overcome the ephemeral behavior of Containers.
I already set up a replicated GlusterFS volume to have data replicated throughout the cluster if I would like to have some persistent data.
The below diagram explains how the replicated volume works.
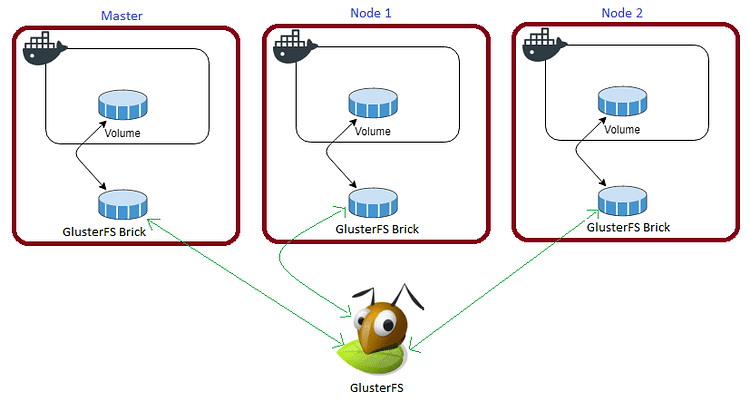
Volume will be mounted on all the nodes, and when a file is written to the
/mntpartition, data will be replicated to all the nodes in the Cluster
Note
Persistent application state or data needs to survive application restarts and outages. We are storing the data or state in GlusterFS and had periodic backups performed on it.
Mattermost will be available if something goes wrong with any of the nodes on our Docker Swarm Cluster. The data will be available to all the nodes in the cluster because of GlusterFS Replicated Volume.
I am going to create 4 folders mattermostconfig, mattermostdata, mattermostlogs and mattermostplugins in /mnt directory to map container volumes /mattermost/config, /mattermost/data, /mattermost/logs and /mattermost/plugins respectively.
cd /mnt
sudo mkdir -p mattermostconfig
sudo mkdir -p mattermostdata
sudo mkdir -p mattermostlogs
sudo mkdir -p mattermostplugins
Tip
Prepare Mattermost Environment
I am going to use docker-compose to prepare the environment file for deploying Mattermost. The compose file is known as YAML ( YAML stands for Yet Another Markup Language) and has extension .yml or .yaml
I am going to create application folders in
/optdirectory on manager node in our docker swarm cluster to store configuration files, nothing but docker compose files (.yml or .yaml).
Also, I am going to use the caddy overlay network created in the previous Caddy post.
Now it’s time to create a folder, mattermost in /opt directory to place configuration file, i.e, .yml file for Mattermost.
Use the below commands to create the folder.
Go to /opt directory by typing cd /opt in Ubuntu console
make a folder, mattermost in /opt with sudo mkdir -p mattermost
Let’s get into mattermost folder by typing cd mattermost
Now create a docker-compose file inside the WordPress folder using sudo touch mattermost.yml
Open mattermost.yml docker-compose file with nano editor using sudo nano mattermost.yml and copy and paste the below code in it.
Mattermost Docker Compose
Here is the docker-compose file for Mattermost. I am going to utilize Postgresql as a back-end database for it.
version: "3.7"
services:
mattermost:
image: mattermost/mattermost-team-edition
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
- /mnt/mattermostconfig:/mattermost/config
- /mnt/mattermostdata:/mattermost/data
- /mnt/mattermostlogs:/mattermost/logs
- /mnt/mattermostplugins:/mattermost/plugins
ports:
- '8065:8065'
environment:
- DOMAIN=mattermost.example.com
- MM_SQLSETTINGS_DRIVERNAME=postgres
- MM_SQLSETTINGS_DATASOURCE=postgres://postgres:postgres@db:5432/mattermost?sslmode=disable&connect_timeout=10
- MM_SERVICESETTINGS_SITEURL=https://mattermost.tuneit.me
- TZ=Asia/Kolkata
networks:
- caddy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == worker]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
db:
image: postgres:alpine
volumes:
- /mnt/postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data
secrets:
- post_db
- post_user
- post_password
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB_FILE=/run/secrets/post_db
- POSTGRES_USER_FILE=/run/secrets/post_user
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/post_password
networks:
- caddy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
secrets:
post_db:
file: ./post_db.txt
post_user:
file: ./post_user.txt
post_password:
file: ./post_password.txt
volumes:
mattermostdata:
driver: "local"
mattermostlogs:
driver: "local"
mattermostplugins:
driver: "local"
postgres:
driver: "local"
networks:
caddy:
external: true
Create secrets mentioned in the above mattermost.yml file in the directory where the file was created.
Caddyfile – Mattermost
The Caddyfile is a convenient Caddy configuration format for humans.
Caddyfile is easy to write, easy to understand, and expressive enough for most use cases.
Please find Production-ready Caddyfile for Mattermost.
Learn more about Caddyfile here to get familiar with it.
{
email you@example.com
default_sni mattermost
cert_issuer acme
# Production acme directory
acme_ca https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Staging acme directory
#acme_ca https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
servers {
protocol {
experimental_http3
allow_h2c
strict_sni_host
}
timeouts {
read_body 10s
read_header 10s
write 10s
idle 2m
}
max_header_size 16384
}
}
mattermost.example.com {
log {
output file /var/log/caddy/mattermost.log {
roll_size 20mb
roll_keep 2
roll_keep_for 6h
}
format console
level error
}
reverse_proxy mattermost:8065
encode gzip zstd
}
Please go to Caddy Post to get more insight to deploy it in the docker swarm cluster.
Final Mattermost Docker Compose (Including caddy server configuration)
Please find the full docker-compose file below. You can deploy as many sites as you want using it.
Don’t forget to map site data directories like
/mnt/mattermostdata:/mattermost/datain Caddy configurationcaddy.yml.
I already wrote an article Caddy in Docker Swarm. Please go through if you want to learn more.
version: "3.7"
services:
caddy:
image: tuneitme/caddy
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
networks:
- caddy
volumes:
- ./Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
- /mnt/caddydata:/data
- /mnt/caddyconfig:/config
- /mnt/caddylogs:/var/log/caddy
- - /mnt/mattermostdata:/mattermost/data
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- node.role == manager
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
mattermost:
image: mattermost/mattermost-team-edition
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
- /mnt/mattermostconfig:/mattermost/config
- /mnt/mattermostdata:/mattermost/data
- /mnt/mattermostlogs:/mattermost/logs
- /mnt/mattermostplugins:/mattermost/plugins
ports:
- '8065:8065'
environment:
- DOMAIN=mattermost.example.com
- MM_SQLSETTINGS_DRIVERNAME=postgres
- MM_SQLSETTINGS_DATASOURCE=postgres://postgres:postgres@db:5432/mattermost?sslmode=disable&connect_timeout=10
- MM_SERVICESETTINGS_SITEURL=https://mattermost.tuneit.me
- TZ=Asia/Kolkata
networks:
- caddy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == worker]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
db:
image: postgres:alpine
volumes:
- /mnt/postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data
secrets:
- post_db
- post_user
- post_password
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB_FILE=/run/secrets/post_db
- POSTGRES_USER_FILE=/run/secrets/post_user
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD_FILE=/run/secrets/post_password
networks:
- caddy
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
secrets:
post_db:
file: ./post_db.txt
post_user:
file: ./post_user.txt
post_password:
file: ./post_password.txt
volumes:
mattermostdata:
driver: "local"
mattermostlogs:
driver: "local"
mattermostplugins:
driver: "local"
postgres:
driver: "local"
networks:
caddy:
external: true
Here I used a custom Caddy docker container with plugins, like Cloudflare DNS, Caddy Auth Portal etc…
Please find the custom caddy docker image below.
Deploy Mattermost Stack using Docker Compose
Now it’s time to deploy our docker-compose file above, mattermost.yml using the below command
docker stack deploy --compose-file mattermost.yml mattermost
In the above command, you have to replace mattermost.yml with your docker-compose file name and Mattermost with whatever name you want to call this particular application.
With docker compose in docker swarm what ever we are deploying is called as docker stack and it has multiple services in it as per the requirement.
As mentioned earlier I named my docker-compose as mattermost.yml and named my application stack as mattermost
Check the status of the stack by using docker stack ps mattermost
Check caddy stack logs using docker service logs mattermost_mattermost
One thing we observe is that it automatically re-directs to https with Letsencrypt generated certificate. The information is stored in /data a directory.
I will be using this
caddy stackas a reverse proxy / load balancer for the applications I am going to deploy to Docker Swarm Cluster.
Also I use docker network
caddyto access the applications externally.
Access / Install Mattermost
Now open any browser and type mattermost.example.com to access the site. it will automatically be redirected to https://mattermost.example.com ( Be sure to replace example.com with your actual domain name).
Warning
Please find below images for your reference. Click on them to open in lightbox for full resolution.
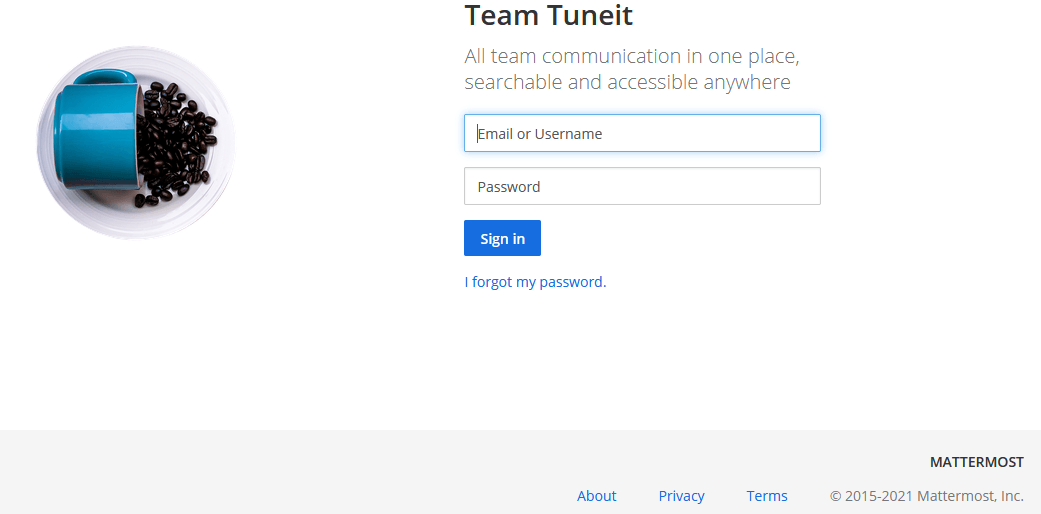
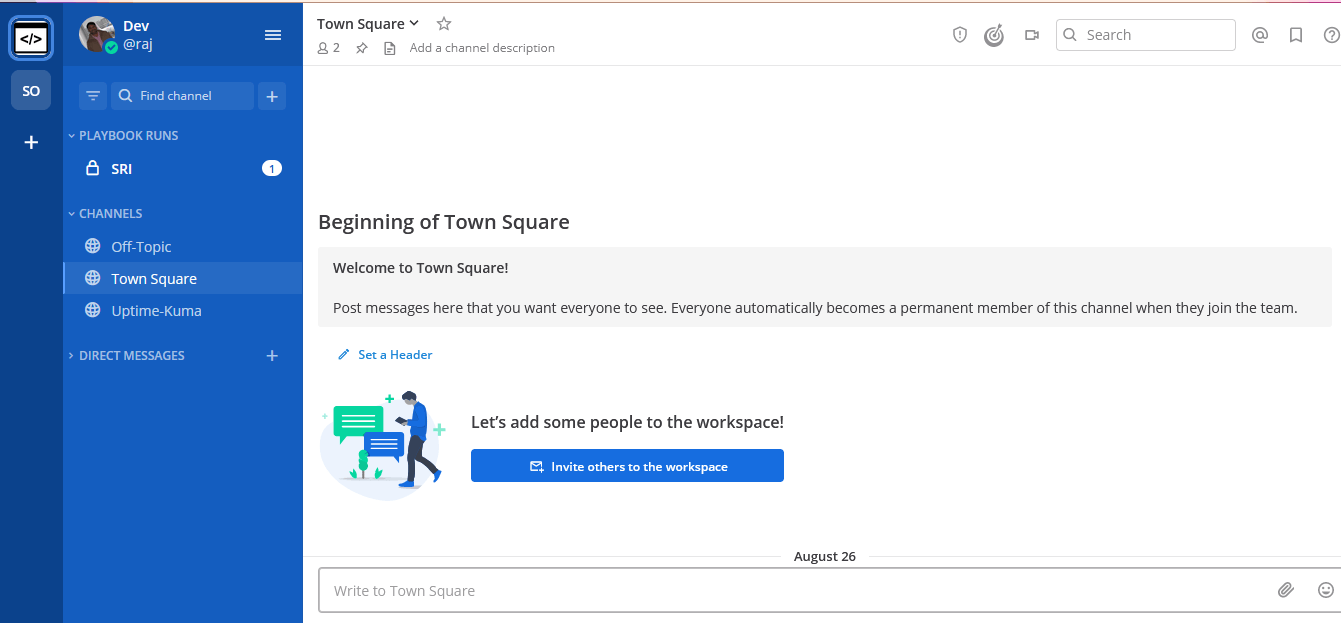
Deployment of Mattermost behind Caddy in our Docker Swarm is successful
If you enjoyed this tutorial, please give your input/thought on it by commenting below. It would help me to bring more articles that focus on Open Source to self-host.
Stay tuned for other deployments in coming posts… 🙄